The first line of treatment for patients at the Kauvery Advanced Spine Center is always a combination of non-surgical therapies. About 90% of patients with no serious spinal ailments can be managed with non-surgical adjuvant therapy initially and they can improve with conservative treatment, including spinal injection, physical therapy, rehabilitation, medication etc.
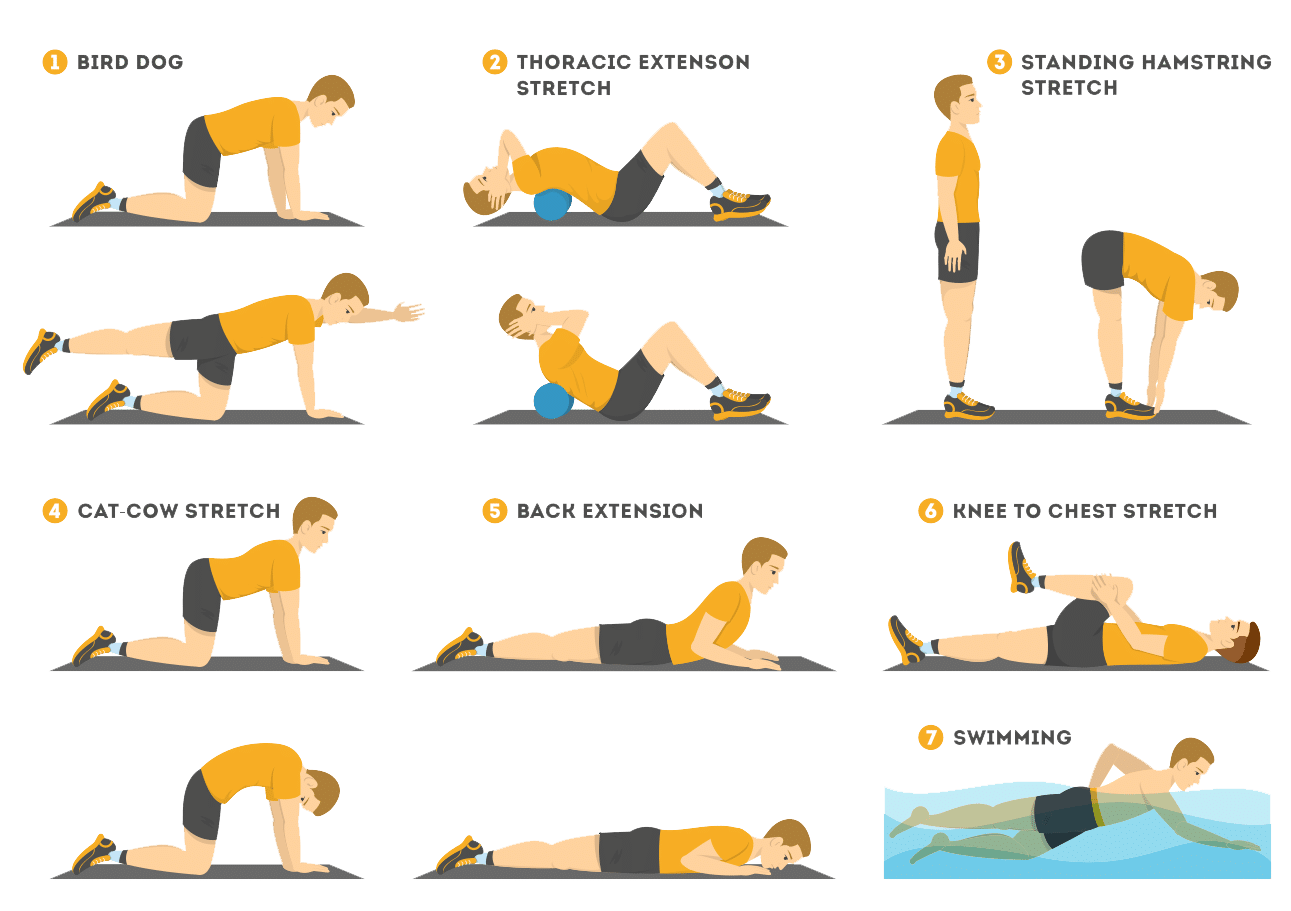
Physiotherapy is the treatment of disease, injury, or deformity by physical methods such as massage, heat treatment, and exercise rather than by drugs or surgery. Physiotherapists are professionals who are specifically trained to help people through movement and exercises, manual therapy, education and advice. However, your involvement is a must for the success of the therapy and they cannot do the exercises for you!
Physiotherapy is extremely effective for back and neck pains. In one study, 80 per cent of people who had physiotherapy for this problem were able to carry on working and did not have to go off sick. If you see a physiotherapist early enough, it can not only speed up recovery but also prevent the problem happening again. They will also advise you on appropriate exercise and pain relief.
There is no controversy that physical activity is harmful for the body when there is no serious problem. The following are the benefits of doing regular exercise. Your exercise should be according to your age, physical ability, medical conditions and feasibility.

This injection technique is done commonly in lumbar canal stenosis associated with severe back pain or persistent leg pain, and also in multilevel disc prolapsed. The effectiveness of this injection is dependent on many factors like severity of the disease, duration of the symptoms, degree of nerve compression and individual variability. The best way to decide about taking the injection is by having a thorough discussion with your doctor regarding the benefits and risks involved and then making a combined decision.
The injection cannot widen the spinal canal, repair the disc damage or reposition/ dissolve the slipped disc. It alleviates the pain by washing off the inflammatory chemicals at the diseased site and steroid suppress the inflammation already set-in. Thus the chemical irritant and physical compression by inflammatory swelling are reduced, providing the pain relief. The local anaesthetic drug also soothens the damaged nerve.
In this method, the medicines are deposited at around a particular nerve root that is being compressed by the slipped disc. The mechanism is similar to that of epidural steroid injection, but it is more specific and targeted.
In case of facetal arthritis or cyst, inflammation can cause severe pain with movement in the back or neck. The medicines are injected directly into the facet joints under X-ray or CT scan guidance. The pain relief works in the same way as mentioned above.
Sacroiliac joint pain usually presents as buttock pain and can be due to degeneration, inflammatory disorder or infection. Inflammatory disorder is most common and the injection technique can be utilized for pain relief after ruling out infection.
This procedure is done in an operating theatre for its sterile environment and under local anaesthesia. Patient will be conscious throughout the procedure and can actually interact with the doctor during the procedure itself. If the patient is anxious or afraid, mild sedatives can be given. The radiofrequency probes are placed at the preplanned targeted site under x-ray guidance and then ablation is done using the RF waves which may take up to 90 seconds. It is a day-care procedure and the person can go home after 2-3 hours of observation in the hospital. There may be procedure related pain in your neck or back which usually subsides within 2 weeks.
The procedure is safe with 70-80% efficacy in pain-relief and the complications are very rare in experienced hands. Minor complications include temporary increase in nerve pain, neuritis, neuroma, localized numbness, infection, allergic reaction to medications used during the procedure, and/or lack of pain relief (in less than 30% of patients).










Copyright ©2024 All Rights Reserved | Book An Appointment